Volkswagen 01M Transmission. Manual - part 37
7
Technical Service Information
ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS
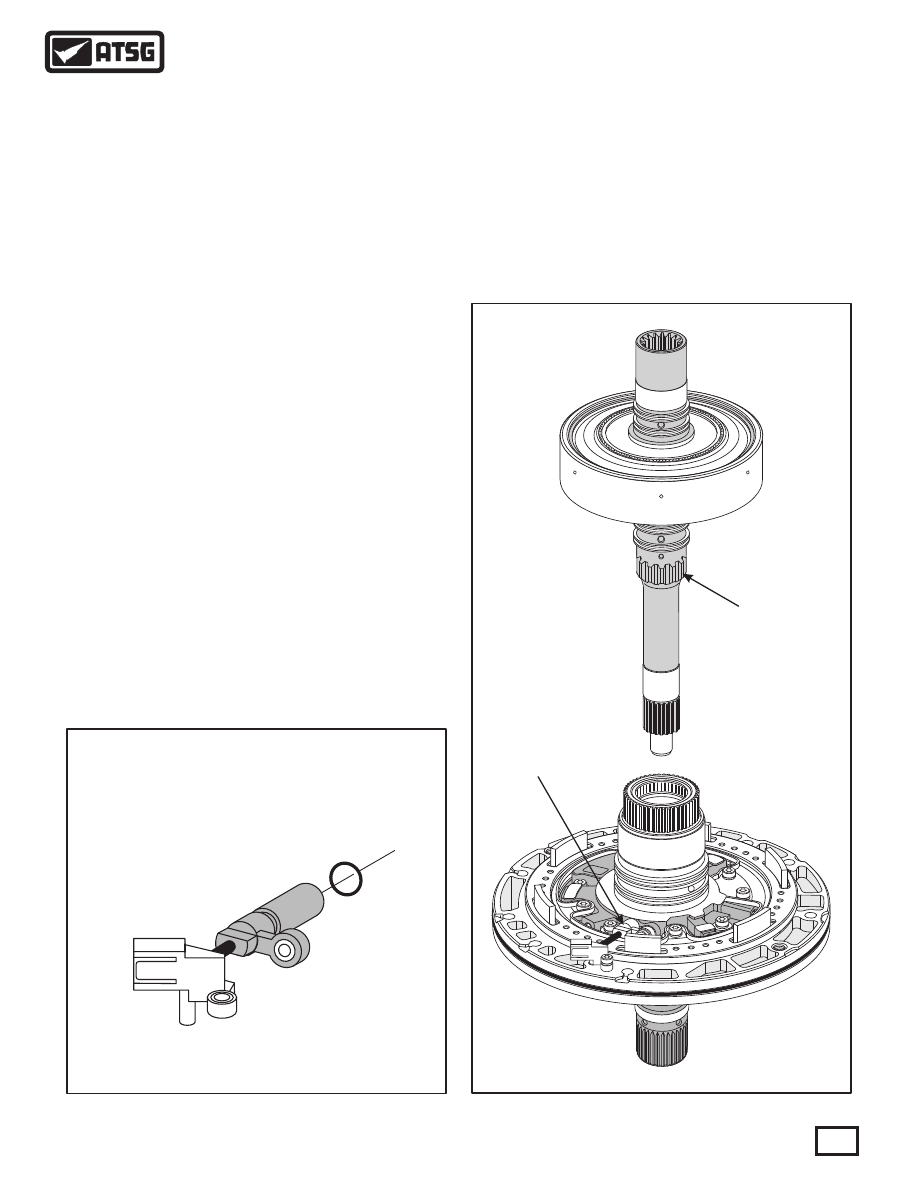
Input Speed Sensor (G182)
The Input Speed Sensor (G182) is located in the
transmission oil pump stator, as shown in Figure 7,
and retained with a bolt. The ISS has a Yellow
connector that mounts on the back side of the oil pump
body and is also retained with a bolt, as shown in
Figure 7. The ISS signal is routed through the 8-way
case connector.
The ISS is triggered by rotor teeth on the turbine
shaft to determine exact transaxle turbine speed, as
shown in Figure 7. The TCM uses this information to
control line pressure for garage shifts, control and
monitor torque converter lock-up clutch, monitor
gear ratios and diagnosis of shift components via the
Dynamic Shift Program (DSP), which is VW's name
for the shift adapt feature in the TCM.
The ISS is based on the Hall Effect principle. The
signal is a square-wave signal whose frequency is
proportional to turbine shaft speed. Should the Input
Speed Sensor fail, the engine RPM sensor is used as a
back-up, but when engine RPM sensor is used there
will be no shift adapt operations, no controlled pulse
width modulation for TCC lock-up (apply and
release only) and no pressure control on garage shifts
(N-D, N-R) which will create harsh garage shift
engagements.
The Input Speed Sensor is shown in Figure 6.
INPUT SPEED SENSOR (G182)
5.0M Ohms Resistance
at room temperature
ISS (G182)
Location
ISS (G182)
Rotor Teeth
3 U
Figure 6
Figure 7
Special Note:
The ISS and OSS are Hall Effect Sensors and
should be checked using a scope under operating
conditions. The resistance values provided in the
Figures below are from new sensors. Resistance
checks on these type of sensors would, at best,
inform you of either open or grounded circuits
within the sensor itself.